MS Pronator Drift Test Device
Quantifiable and objective tracking of downward arm drift in Multiple Sclerosis patients using ultrasonic sensors and Arduino.
Problem Statement
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) affects 2.8 million people globally, with 83.6% experiencing pyramidal impairments that can be detected through pronator drift tests. Currently, these tests rely on subjective clinical assessment, leading to inconsistent results between different clinicians and limiting objective disease tracking.
Solution
Our team developed a device that objectively measures and quantifies the downward shifting of arms during pronator drift tests. The device can be used in patients' homes, reducing hospital visits while providing clinicians with quantifiable data for better disease progression tracking.
Technical Design
Hardware Components
- Arduino Uno: Central processing unit
- Ultrasonic Sensors (2x): HC-SR04 40kHz sensors for distance measurement
- LCD Display: Real-time feedback and results display
- Buzzer: Audio feedback during testing
- Button & Potentiometer: User interface controls
- 9V Battery: Portable power supply
Mechanical Design
- Base: 410mm × 200mm laser-cut acrylic platform
- Sensor Mounts: 3D-printed ABS plastic holders
- Assembly: Modular design with threaded inserts and screws
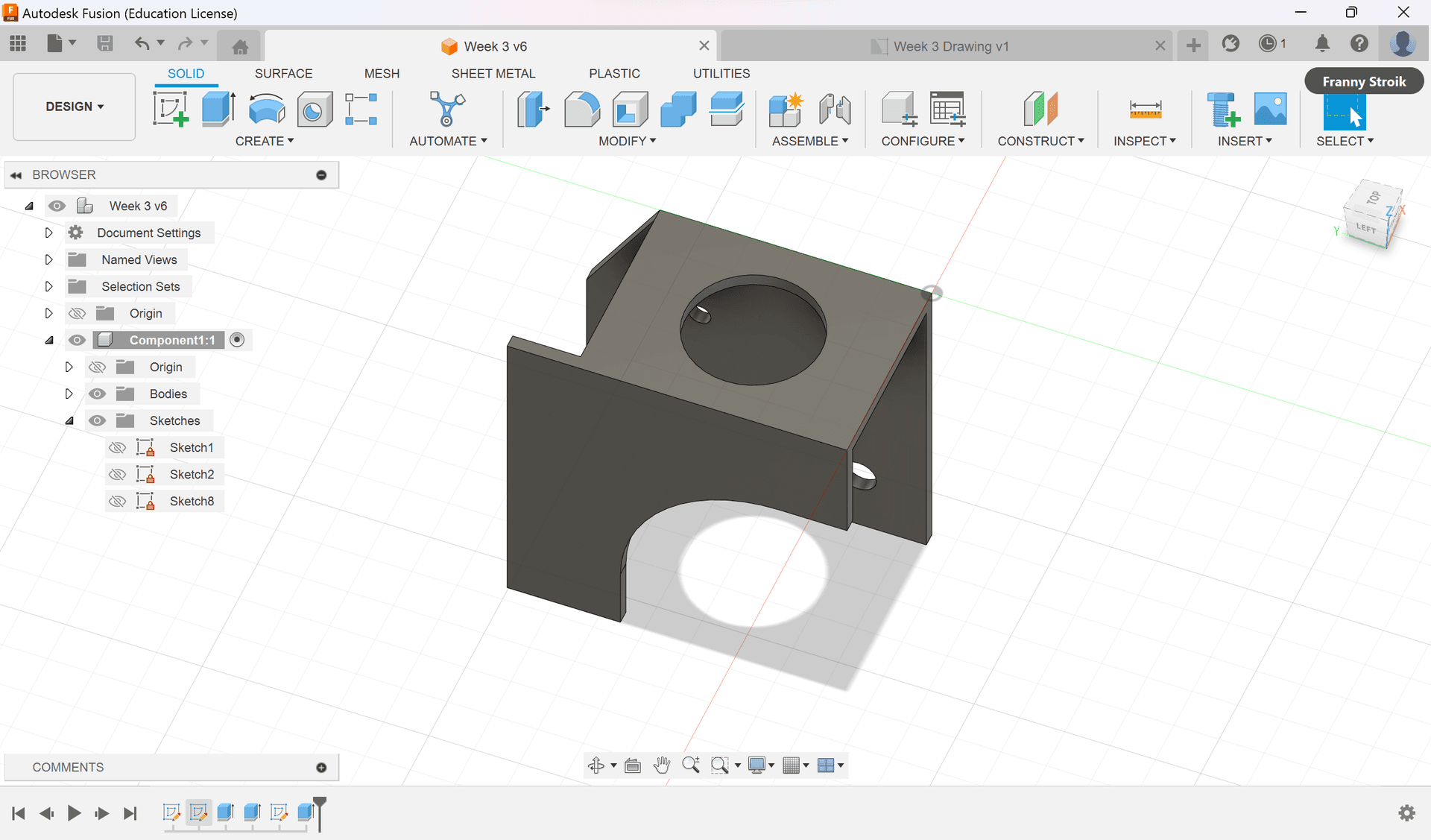
CAD design of mechanical components using Fusion 360
How It Works
- Patient places device on flat surface and positions hands above sensors
- System initiates 20-second test with audio prompts
- Ultrasonic sensors continuously measure hand height
- Device calculates differential drift between hands
- Results displayed showing average drift and affected side
Technical Innovation
The ultrasonic sensors emit sound waves and measure return time to calculate distance. By monitoring both hands simultaneously, the device can detect asymmetric drift patterns characteristic of MS-related pyramidal dysfunction.
Clinical Impact
This objective measurement tool enables:
- Consistent, quantifiable assessment across different clinicians
- Home-based monitoring reducing patient hospital visits
- Early detection of MS relapses through regular monitoring
- Data-driven treatment decisions based on measurable progression
Team Collaboration
Worked as part of the "Charming Chinchillas" team including Jessica Bailey, Amogh Sandil, Juliette Steffenson, Anna Young, and Ethan Yu. The project utilized ChatGPT assistance for code development and successfully demonstrated the feasibility of objective MS assessment tools.